False Color display mode
 Version 7 and greater of videoQC, and DrasticScope at the 4KScope, HDRScope, and 2110Scope levels all include a false color display mode. False color mode looks at the IRE values in the signal, and assigns a color to each range. Here are details.
Version 7 and greater of videoQC, and DrasticScope at the 4KScope, HDRScope, and 2110Scope levels all include a false color display mode. False color mode looks at the IRE values in the signal, and assigns a color to each range. Here are details.
4KScope, HDRScope, 2110Scope, and videoQC all feature Drastic's display modes, including False Color mode.

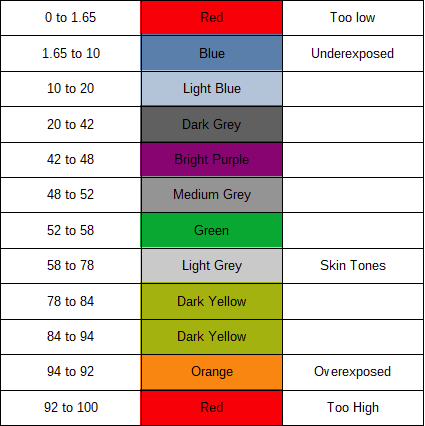
False Color mode breaks the image up into its IRE/exposure levels, and assigns a color to each level. Here are the colors and their levels:
The IRE unit is used in the measurement of composite video signals. Its name is derived from the initials of the Institute of Radio Engineers.
A value of 100 IRE is defined to be +714 mV in an analog NTSC video signal. A value of 0 IRE corresponds to the voltage value of 0 mV, the signal value during the blanking period. The sync pulse is normally 40 IRE below this 0 IRE value, so the total range covered from peak to trough of an all white signal would be 140 IRE.
The PAL video signal is slightly different in that it swings from -300 mV to +700 mV, instead. Thus, one PAL IRE unit is 7 mV, where -43 IRE is equivalent to -300 mV at the sync tip, and +100 IRE is equivalent to +700 mV at the peak video level. Black level is the same as the blanking level 0 mV (0 IRE).
The reason IRE is a relative measurement (percent) is because a video signal may be any amplitude. This unit is used in the ITU-R BT.470 which defines PAL, NTSC and SECAM.
In the below image, the signal on the left is unaltered. The signal on the right is displayed in false color mode.

Trademarks, Registered Trademarks, and CopyrightsTrademarks, Registered Trademarks, and Copyrights
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers - IRE is a trademark of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.

